Null pointers in a Binary tree
January 23, 2013using delete operator on this
January 29, 2013Printing border nodes of Binary Tree
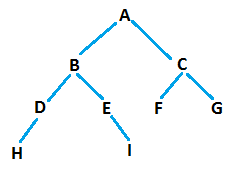 Given a Binary tree, Write code to print all the boundary nodes in counter clockwise order. For example, for the below binary tree,
Given a Binary tree, Write code to print all the boundary nodes in counter clockwise order. For example, for the below binary tree,
The output should be: A, B, D, H, I, F, G, C, A . Boundary Nodes are traversed in anti-clockwise order.
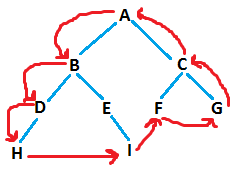
Solution:
The algorithm can be divided into three modules
Module-1: Print Nodes on Left boundary in top-down order. Module-2: Print all the leaf nodes, in left-to-right order. Module-3: Print Nodes on Right boundary in bottom-up manner.
We have to be cautious about not to print a node twice. For example, the last node in left boundary traversal (‘H’) will be printed by both Module-1 and Module-2. Similarly, Node ‘G’ will be printed by both Module-2 and Module-3.
Hence, we should print all nodes except the last (leaf node) in Module-1 and Module-3.
Let’s look at the code of individual modules now.
Module-1: Printing Nodes on left boundary (from top-to-bottom).
This is fairly simple. Just keep in mind that if a node does not have left child, then its right child is on the left boundary. For example, in the tree below tree
A
/ \
B C
\
D
/
E
D is on the left boundary.
/**
* Print Nodes on the left boundary in top-down manner.
* Does not print the last node because it will be printed along the leaf nodes.
*
* If a particular node does not have left child,
* then its right child will be at the left boundary.
*/
void printLeftSide(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
while( root->lptr != NULL || root->rptr != NULL)
{
cout<<root->data<<" ";
if(root->lptr)
root = root->lptr;
else
root = root->rptr;
}
}
Module-3: Printing Nodes on right boundary (in bottom-up manner).
It make sense to write a recursive function for this, because we are printing in bottom-up and there is no link in upward direction (both lptr and rptr points downward).
/**
* Print Nodes on the Right boundary in bottom-up manner
* Does not print the last node because it will be printed along the leaf nodes.
*
* If a Node does not have right child,
* then its left child will be printed.
*/
void printRightSide(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
if(root->lptr != NULL && root->rptr != NULL)
{
if(root->rptr)
printRightSide(root->rptr);
else
printRightSide(root->lptr);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
}
}
Module-2: Printing Leaf Nodes (left-to-right).
Print all the leaf nodes from left to right. This is simple recursive function of tree.
void printLeafs(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL )
return;
if(root->lptr == NULL && root->rptr == NULL)
{
cout<<root->data<<" ";
}
else
{
printLeafs(root->lptr);
printLeafs(root->rptr);
}
}
And finally the main callable function which connects the above three functions.
void printBorderNodes(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root->lptr)
printLeftSide(root);
printLeafs(root);
if(root->rptr)
printRightSide(root);
}
In the above function Node structure of Tree is defined as below:
struct TreeNode
{
char data;
TreeNode* lptr;
TreeNode* rptr;
};
